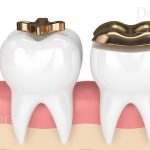

Periodontitis is a very common serious gum infection that means inflammation of soft tissue around the teeth. It damages to soft bones and tissue supporting teeth.
All periodontal diseases, including periodontitis, effect on periodontium. This is an ongoing disease that occurs slowly and destroy the bone tissue around the teeth. Microorganism like bacteria, attach to the surface of the teeth and then multiply. Those patients with high immune system react them to inflammation.
Untreated periodontitis will lead to teeth loss, increasing the risk of heart attack or the other health problems.
Bacteria plaque (a sticky, colorless membrane that create over the tooth surface) is the most common reason of periodontal disease. Periodontitis is the knowledge of prevention, diagnosis and treatment of gum and structural disease that protect of teeth. Generally, there is 8 specialized fields in dentistry major, periodontics is one of them. If you want to do implant you should see a periodontics. Usually, periodontitis is predictable and occur due to inappropriate oral hygiene.
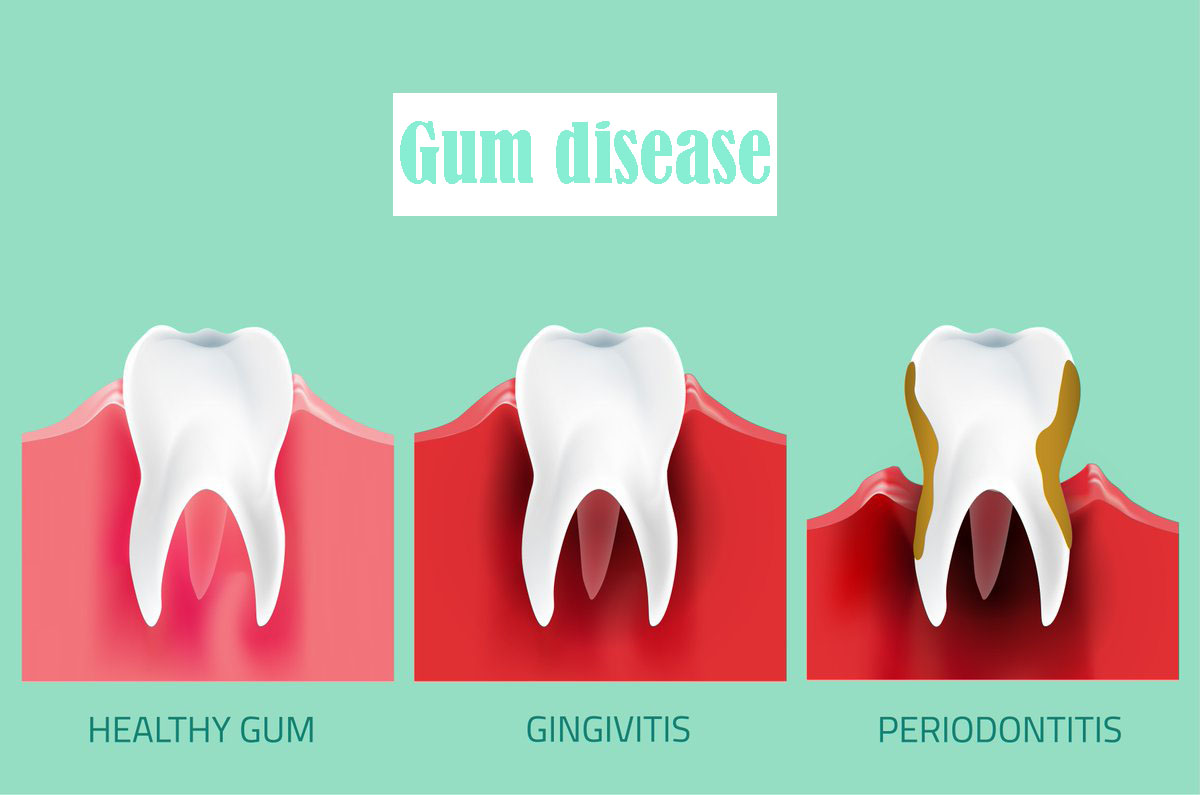
What is the difference between periodontitis and gingivitis?
Gingivitis occur before periodontitis and usually refers to gum inflation, while periodontitis is a disease that tissue and bones are destroyed. Initially, bacteria plaque collects on the surface of tooth and causes gum to become red and inflamed, in this case teeth may bleed during brushing. Although gums are stimulated and annoyingly but gingivitis is not leads to tooth loos and serious damage to bones and surrounding tissue. Read certainly: How plaques are formed on teeth? and scaling.
Untreated gingivitis leads to periodontitis and it causes to gums and bones loose and form large space between teeth. The small space between gums and bones gather debris and become infected that location. While the plaque is spread under the gum, immune system attacks bacteria and destroy bonds and surrounding gums that protect of teeth, it may lead to loos and fall out teeth. In simple words, periodontitis includes the irreversible changes of tissues surrounding teeth while gingivitis doesn’t have the same condition.
What is the cause of periodontitis?
Bacteria plaque is the cause of periodontitis. Plaque is a sticky substance that create on the surface of teeth a couple of hours after brushing. It is interesting to know that body reaction to bacterial infection makes most of the problems. Immune system’s cells when are trying to remove bacteria, produce a substance that causes inflammation, gum destruction, periodontal ligament or alveolar bone. This procedure, leads to swollen, bleeding gums, signs of gingivitis (that is the first stage of periodontal disease) and loosing of the teeth that is a symptom of sever periodontitis (the advanced stage).
It’s another issue if plaque create on tooth surface, it becomes hardened and calcified and turn into calculus that usually called tartar. Since calculus is rougher than tooth enamel or cementum (it is a layer that cover the tooth root), by continuing collection, more plaque will attach to tooth. Using a tartar control toothpaste can to reduce the collection procedure around the tooth. It doesn’t have any effect on those tartar that have already collected between tooth and gum spaces.

Symptoms
Healthy gums, are light pink color and accurately cover around teeth. The periodontitis signs and symptoms are as bellow:
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Bright red, dusky red or purplish gums
- Gums that feel sensitivity when touched
- Gums that bleed easily
- Gums that pull away from teeth and makes teeth to looks longer than normal
- Developing new space between teeth
- Making pus between teeth and gums
- Bad breath
- Loose teeth
- Painful chewing
- A change in the way that teeth fit together when biting
Periodontitis disease has several different types and the most commons types are:
- Chronic periodontitis is the most common type among adults, although kids can be affected, too. Increasing numbers of mouth plaque is the cause of this type and over the time cause to get worse and if doesn’t treat, leads to gums destruction, boons and teeth loos.
- Aggressive periodontitis usually begins in childhood or early adulthood and less people are affected by this disease. It mostly effects on family and if doesn’t treat, rapidly leads to progression of bone and teeth loose.
- Necrotizing periodontal disease is described by the death of gum tissue, tooth ligaments and supporting bone caused by lack of blood supply(necrosis), terminating in severe infection. Generally, those who have malnutrition or weak immune system (like HIV infection, cancer treatment etc.) are more expose by this disease.
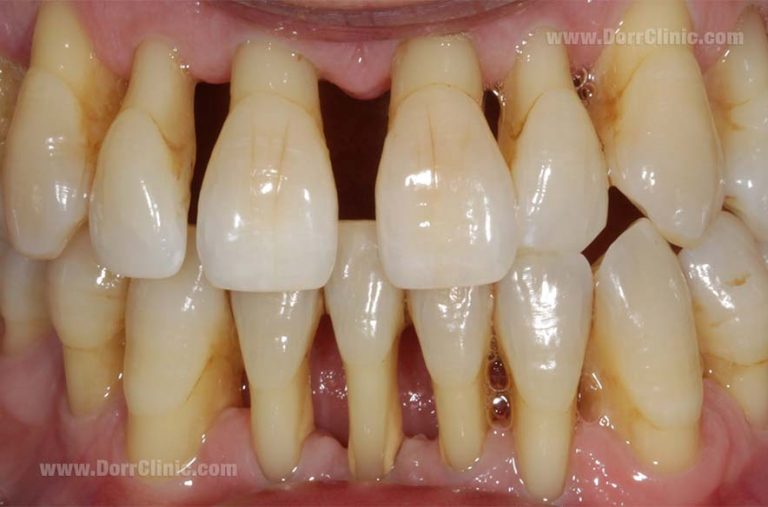
Prevention
Periodontal inflammation is unavoidable and can prevent of periodontitis and the progress of gum inflation by observing oral hygiene, alongside regular examination and tooth care.
Several important factors for considering mouth and teeth health are as bellow:
- Brushing surfaces and sides of the teeth twice a day (your toothbrush should have appropriate size and other characteristic of a good brush).
- Daily cleaning the space between teeth (where toothbrush bristles can’t reach) by dental floss and interdental brushes (depending on the size of space between teeth).
- Flossing should be used where teeth are close together and have less or no space while interdental brushes are suitable for larger space. Special care should consider to clean around crooked or crowded teeth, around filling, crowns and dentures because plaque easily gather in these places and it’s difficult to access.
- Antibacterial mouth washers are suitable supplement to brushing because release the bacterial growth and decrease inflammatory Mouth washers should be use after tooth brushing.
- In case of insufficient cleaning procedure, plaque deposits create on teeth and this gathering turn to hard and fixed substance (calculus, generally known as tartar) that can’t be remove by brushing. Dentist or periodontist during the regular dental checkup, distinguish the tartar deposits and through a professional procedure clean them. After removing deposits, tooth will be polished by special pastes in order to make a smooth surface and decrease possibility of plaque gathering.
What are the risk factors of periodontist?
There are several factors such as stress, some systemic disease like diabetes and smoking which are more important than the others ones, increase the risk of creating and developing periodontist.
Smoking and periodontist
- Mostly smokers are affected with periodontist than nonsmokers.
- The success probability of periodontist treatments (such as implant and gum or bone grafts) are less developed in smokers than nonsmokers due to slow cure procedure for smokers’ body tissues.
- The procedure of periodontist disease and even tooth loos are faster in smokers than nonsmokers.
- 90 percent of those who are not responded by periodontist treatment are smokers.

How is periodontist treated?
Usually by accurate assessment and appropriate treatment method, it’s possible to stop the periodontist progress. The key of a successful treatment is exercise and repetition of oral hygiene practices and removing bacteria plaque that are the main causes of disease progress.
- Oral hygiene guidance and recommendations
The point of treatment methods is to observe oral hygiene, reduce the numbers of mouth bacteria in order to decrease the level of tooth inflammation. Initially, dentist explain to patient the cusses of periodontist disease and then illustrate the exact method of considering and cleaning tooth and gums, such as training the most appropriate tooth brushing method, and the correct use of dental floss and interdental brushes.
Professional cleaning
All the tooth soft deposit can be cleaned from reachable areas and clean and brush tooth by fluoride. By considering the progress rate seen in mouth plaque control and gum health, further training and cleaning procedure will be done in later appointment in case of need. The next step is to illuminate all tartar and bacteria deposits from the root surface and gingival pockets by dentist.
Antibiotic treatment
In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed for active or persistent gum infection that are not treated by observing oral hygiene measurement or without microbiological test.

Reassessment
After several weeks, dentist or periodontist, will assess gums in order to assure of treatment procedure. Dentists use of a device that called probe or periodontal to record the depth of gum inflammation and prevent of gum bleeding. For untreated gum inflammation, some other treatment options like surgical therapy are recommended.
Corrective (surgical) treatment
Sometimes, a surgical procedure is recommended for removing the bacteria plaque and deposits that are created under the gun within periodontal pockets and on the root surface at the furcation. These areas are inaccessible for tooth brushing and tooth flossing and as long as bacteria are placed in these areas, inflammation is unavoidable. Under local anesthesia, gums are lifted away and roots surface are cleaned under the doctor’s accurate vision to ensure of destroying all bacteria. In some cases, can to treat the bone loss by this special technique. By the end of the surgery, again gums are attached on their location.
Aftercare-supportive periodontal therapy
Long term success of periodontal treatment depends on individual effort for observing oral hygiene and some ongoing assessment by a practice team to provide ordered care. After doing the first step of treatment, dentist should consider your gum condition and become sure of inflammation treatment. Regular checkup appointment is depending on diseases severity and the risk of disease progression. Usually these appointments are arranged for every three to six months.
Regular checkup appointments are very important because during these sessions doctor will ensure disease procedures is not continuing and if there is no symptom of diseases progress, it is possible to distinguish the inflammation location and treat them in early stages. Also the appropriate method of oral hygiene is trained to patient in order to prevent of inflammation.
Successful treatment of periodontal disease requires full cooperation of patient and observing oral hygiene and participate at regular checkup sessions.
Ask from the doctor